Present Perfect Tense
timeline, form, uses
The Present Perfect tense is used to talk about a past action. Time is not indicated unless other words in the phrase or sentence specifically express that. It may also be use do express that an action began in the past and continues to the present. Below we’ll explore Present Perfect tense timeline, forms, uses, with examples.
TO FORM THE PRESENT PERFECT TENSE
The Present Perfect is formed using:
– auxiliary verb to have conjugated in the Present Simple (have / has)
– main verb in the Past Participle (ending +ed / +d / irregular)

affirmative: subject + auxiliary + main verb
negative: subject + auxiliary + not + main verb
questions: auxiliary + subject + main verb
negative questions: auxiliary + subject + not + main verb
Forms of the Present Perfect tense for the verb to see:
affirmative
I have seen
you have seen
he/she/it has seen
we have seen
you have seen
they have seen
negative
I have not seen
you have not seen
he/she/it have not seen
we have not seen
you have not seen
they have not seen
questions
have I seen?
have you seen?
has he/she/it seen?
have we seen?
have you seen?
have they seen?
negative questions
have I not seen?
have you not seen?
has he/she/it not seen?
have we not seen?
have you not seen?
have they not seen?
PRESENT PERFECT TENSE USES
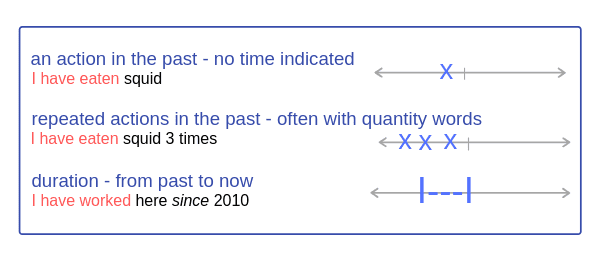
to express an action that started and finished at some time in the past when time is not indicated (use the Past Simple if time is indicated)
I have worked in sales.
Tom has changed his car.
in the negative it can express an action that remains uncompleted
Mark has not finished his homework.
to express a repeated actions in the past
(often with words of quantity i.e. numbers, many)
I have moved house 4 times in my life.
We have been on holiday to Mexico many times.
to express duration with for or since
(the action started in the past and may still be going on)
I have been on holiday for a week.
She has lived here since 2010.
to talk about an experience or accomplishment
He has never eaten meat.
She has learnt to drive.
to talk about change over time
He’s grown since I last saw him
often used after a superlative
This is the funniest film I have ever seen.
CONTRACTED AUXILIARY VERBS
The Present Perfect uses the verb to have in the Present Simple as an auxiliary verb.
Auxiliary verbs are often contracted, especially in spoken and informal written language.
The contracted forms are:
| affirmative | contracted |
| I have | I’ve |
| you have | you’ve |
| he/she/it has | he’s / she’s / it’s |
| we have | we’ve |
| you have | you’ve |
| they have | they’ve |
| negative | contracted |
| I have not | I haven’t |
| you have not | you haven’t |
| he/she/it has not | he/she/it hasn’t |
| we have not | we haven’t |
| you have not | you haven’t |
| they have not | they haven’t |
| negative question | contracted |
| have I not? | haven’t I? |
| have you not? | haven’t you? |
| has he/she/it not? | hasn’t he/she/it? |
| have we not? | haven’t we? |
| have you not? | haven’t you? |
| have they not? | haven’t they? |
More on contracted auxiliary verbs
Present Perfect tense timeline, forms