Asking Questions in English

There are several ways of asking questions in English, depending on the information sought:
YES / NO QUESTIONS
These are questions that we expect to receive a yes or no as an answer, rather than an explanation or longer answer.
The can be formed using:
– auxiliary verbs
– modal verbs
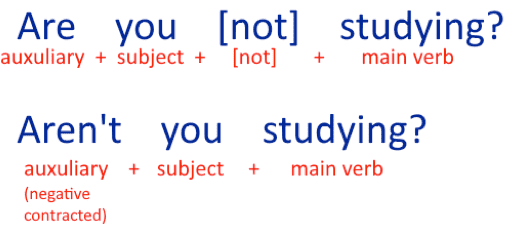
1. YES / NO QUESTIONS WITH AUXILIARY VERBS
The auxiliary verbs to be, to do, to have are used to ask questions when we expect ‘yes’ or ‘no’ as an answer.
The construction is:
auxiliary verb + subject + [not] + main verb
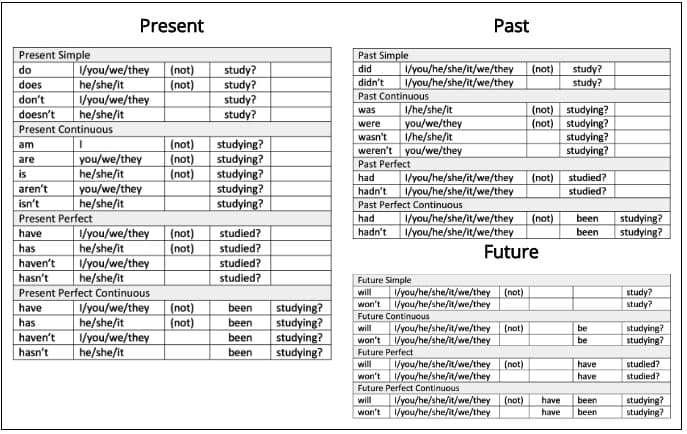
Examples for the Present, Past and Future Tenses
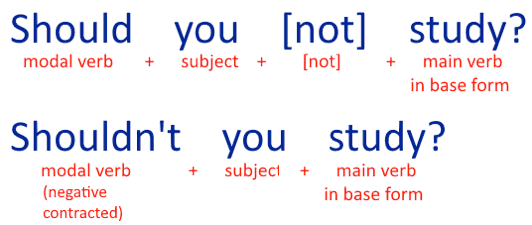
2. YES / NO QUESTIONS WITH MODAL VERBS
Using modal verbs to ask yes/no questions the construction is:
modal verb + subject + [not] + main verb in base form
Can you tell me the time please?
Must I do all the exercises?
May I not have a piece of cake?
Might he come later?
Couldn’t I go?
Shouldn’t she rest?
Remember – modal verbs are a form of auxiliary verbs and include:
can, could, may, might, ought to, must, should, shall, will, would
Review Modal Verbs
WH- QUESTIONS
Wh- words are a range of words used to form questions. Some but not all begin with wh-, and each has a specific use. They may be used with auxiliary verbs, or with modal verbs.
what….? for an object or thing
where..? for a location or place
when…? for a date or time
why…..? for a reason
who…..? for a person
which…? for a choice from a defined group
wh- words also include how questions:
how…? for a method or technique
how much…? for an uncountable nouns or a price
how many…? for a countable noun
how often….? for frequency
how ‘adjective’? for a quality i.e. how tall, how heavy.
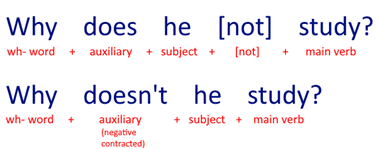
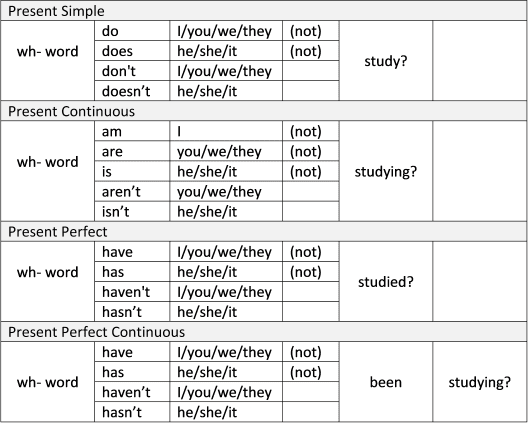
1. WH- QUESTIONS WITH AUXILIARY VERBS
For wh- question words the construction is:
wh- word + auxiliary verb + subject + [not] + verb
Present Tense
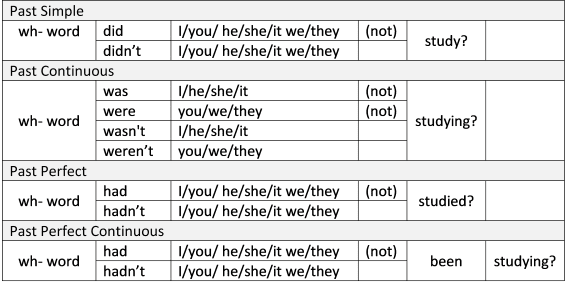
Past Tense
Future Tense

For who, which or what, if they are the subject of the sentence the auxiliary verb is not used
Which toy is your favourite?
What time is the meeting?
2. WH QUESTIONS WITH MODAL VERBS
Using modal verbs to ask wh- word questions the construction is:
wh- word + modal verb + subject + [not] + main verb in base form
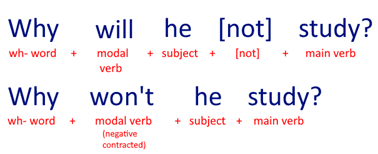
When can he come?
Why should I not play?
Why wouldn’t she go?
Remember – modal verbs are a form of auxiliary verbs and include:
can, could, may, might, ought to, must, should, shall, will, would
Review Modal Verbs
TAG QUESTIONS
A tag question is a statement followed by a short question tag on the end which asks if the listener agrees with the statement.
The tag uses the auxiliary verb or if there is no auxiliary then the verb to do is commonly used
The construction is:
statement sentence + tag
If the statement has an auxiliary verb, including modal verbs, this is used to construct the tag:
It’s freezing, isn’t it?
We are going now, aren’t we?
They were leaving yesterday, weren’t they?
She has been to China, hasn’t she?
You will call me when you get home, won’t you?
He must be so tired, mustn’t he?
If the statement does not contain an auxiliary verb, we often use the verb to do:
Max loves dogs, doesn’t he?
They work at the bank, don’t they?
He wasted so much time, didn’t he?
Note:
when the statement is positive, the tag is negative
when the statement is negative, the tag is positive
That is nice, isn’t it?
That is not nice, is it?
INDIRECT QUESTIONS
Indirect questions are used when we want to be more polite or formal.
An introductory phrase comes before the question:
introductory phrase + question word + positive statement with verb after the subject
Some introductory phrases include:
Could you please tell me…
I would be interested to know…
Would you mind telling me…
I wonder if you could tell me….
Do you know…
USUAL FORM
Where is the Post Office?
What time is the next bus?
When is the carnival?
INDIRECT FORM
Would you mind telling me where the Post Office is please?
Do you know what time the next bus is please?
Could you tell me when the carnival is?
Note the verb comes after the subject, as in a normal positive statement –
… the Post Office is…
… the next bus is…
… the carnival is….
PRACTICE EXERCISES
1. Are these statements True or False
The auxiliary verbs to be, to do, to have are used to form questions when we expect the answer to be yes or no.
When is used to form questions related to time.
A negative question tag is added after a positive statement to form a question.
Indirect questions are a more formal and polite way of asking questions.
2. Complete the questions using the appropriate wh-word
_____ is your name?
_____ is your favourite artist?
_____ did you start learning English?
_____ are you from?
_____ do you work?
3. Turn these statements into questions using question tags.
We’re having fish for dinner tonight.
It’s due to snow tomorrow.
That’s a picture of you when you were young.
Jim was digging the garden.
She has written three books.
Answers
1. all true
2. what, who, when, where, where
3. aren’t we, isn’t it, isn’t it, wasn’t he, hasn’t she